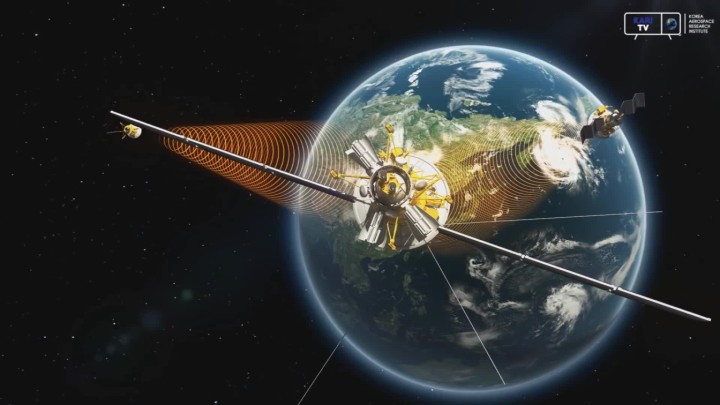
Korea Augmentation Satellite System (KASS)
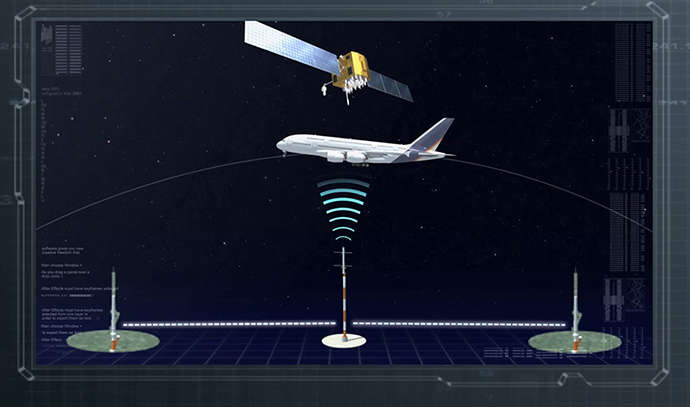
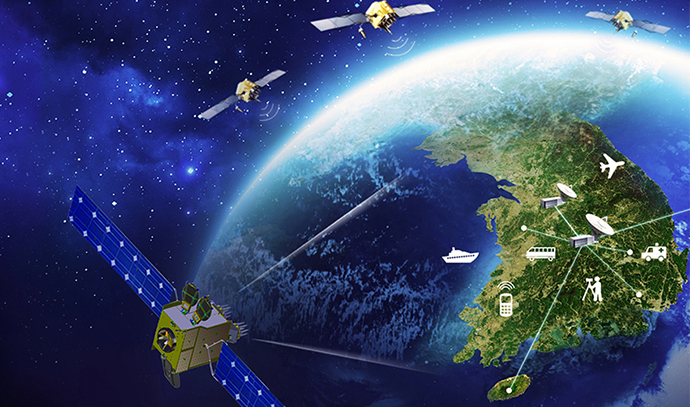
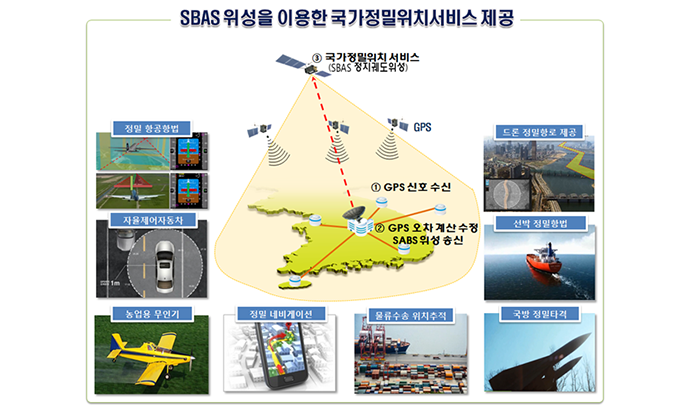
To correct GPS signal errors and provide high-precision location data, Korea developed the Korea Augmentation Satellite System (KASS). KASS utilizes Satellite-Based Augmentation System (SBAS) technology to reduce GPS positioning errors to within three meters. Signal transmission via geostationary satellites began in 2022, and following preparations for aviation-specific services in 2023, Korea became the fifth country—after the United States, the European Union, Japan, and India—to operate an SBAS system for aviation. As a critical infrastructure component, KASS is expected to support not only the aviation sector but also industries such as autonomous driving, drones, maritime operations, and national defense by providing accurate and reliable location information.
-
October 2014
Project Initiation
-
December 2022
KARI was designated as the official agency responsible for managing and operating KASS, classified as a radio navigation safety facility
-
March 2023
Service agreement signed with the Office of Air Traffic, with operational centers established in Cheongju and Incheon
-
February 2024
After 9 years and 4 months of development and deployment, the KASS system was officially transferred to the government.
Improvement of GPS location error to less than 3 meters
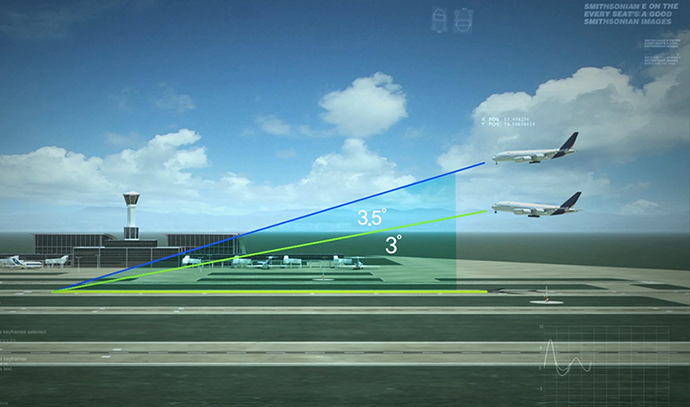
The current GPS location error is about 10 meters, limiting its use in fields that require precision location information such as aircraft. To address such limitations, Europe (EGNOS), Unites States (WAAS), India (GAGAN), and Japan (MSAS) are operating the Satellite Based Augmentation System (SBAS), which improves the accuracy and reliability of GPS signals.
SBAS improves the GPS location error to less than 3 meters and provides the information needed to confirm its reliability throughout the country through geostationary orbit satellites. Since the data is very reliable with an error probability of less than 1/5 million (error occurring once every 18 years), the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) aims to increase its use in flight airspace to support the continuously growing air traffic volume. The organization has designated SBAS as the international standard, recommending that countries operate and use the service to increase satellite navigation accuracy and reliability.
Korea is developing and implementing the Korea Augmentation Satellite System (KASS), an independent satellite-based augmented navigation system, since 2014 as a project by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, and Transport. KASS is being developed under SBAS international standards to meet Korea’s accuracy and reliability requirements and suit the country's topography and environment. KASS enables Korea to use satellite-based technology as well instead of depending on ground-based navigation safety facilities.
The goal of KASS, which is the world’s 7th development of SBAS, is to provide air navigation information and various kinds of location-based information close to people’s lives. Its development started in October 2014 with KARI as the project manager, and the aviation service is scheduled to start in 2023 after the system design, production, and performance certification.
Use for aircraft safety and emergency rescue
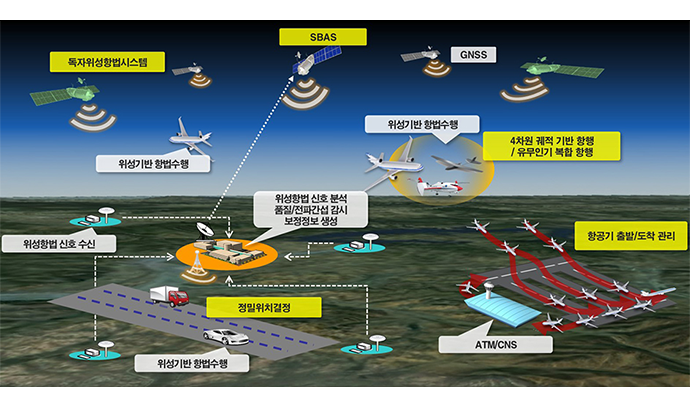
KASS receives GPS signals from domestic ground reference stations (7 locations), extracts navigation messages, and transmits them to the central processing stations (2 locations). Subsequently, the central processing station corrects the GPS error information and generates correction and integrity information necessary to notify whether the GPS signal is normal. It then transmits the data to the satellite communication station, which in turn generates SBAS signals (SBAS messages) and transmits them to geostationary orbit satellites. The information is finally broadcast by the geostationary orbit satellites throughout the country. A receiver installed in an aircraft or a vehicle can receive GPS signals and SBAS signals at the same time to check their exact location. If there is an error in the signal, the automatic SBAS alarm system provides an alarm notifying the prevention of use within 10 seconds so that the users can have confidence with the data.
|
1 To receive GPS location information
|
2Error value correction and integrity data for satellites
|
3Correction of signal satellite service
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 Reference Station
|
2 Central Processing Station
|
3 Satellite Communication Station
|
4 geostationary satellites
|
| Reference Station (7 Locations) |
Central Processing/Integration Station (2 Locations) |
Satellite Communication Station (2 Locations) |
SBAS Satellite (Leased) |
| GPS signal reception SBAS signal reception | GPS error calculation, SBAS data generation and control | SBAS signal transmission to satellites | Delivery of SBAS signals throughout the country |