Developed by exclusive Korean technology through the know-how of operating satellites
다In the initial operation of the test lunar orbiter (KPLO), 24-hour communication is made possible with 4 overseas ground stations in Italy, Australia, Chile, and Hawaii via SSC (Swedish Space Corporation)’s network operation center (Esrange). The remote operation with network operation centers of overseas ground stations is performed at KARI’s satellite operation center. After launch and initial operation of the test lunar orbiter (KPLO), the Korean ground station will be operated starting from in-orbit testing (2 weeks after launch). The ground system of the test lunar orbiter (KPLO) will be developed through technologies and expert human resources acquired from operating low orbit satellites. The ground system consists of the transmission/reception subsystem in charge of communication between the satellite & ground and reception & broadcasting of images; real-time operation subsystem for satellite operation and control; control system such as the mission planning subsystem and aerodynamic subsystem; data pretreatment system for real-time reception, processing and distribution of payload images; and integrated monitoring subsystem of the entire ground system.
- Composition of Ground System: Transmission/reception subsystem, control system, data pretreatment system, integrated monitoring subsystem
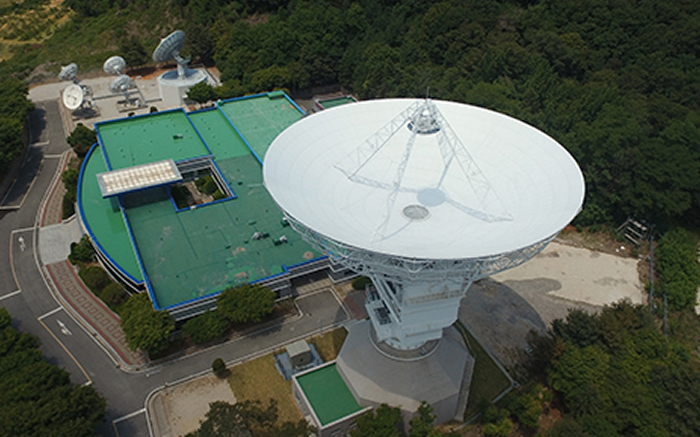
- Korea’s first ground system for deep space communication, built for the operation of Danuri
- Consists of the Korea Deep Space Antenna (KDSA) and the Korea Mission Operation Center (KMOC)
- Supports key operations including communication with Danuri, status monitoring, and reception of command and telemetry data
Required Technologies for Lunar Orbital Exploration
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Spacecraft Bus |
|
| Mission/System |
|
| Payloads |
|
| ILN |
|
| Ground Station |
|
Why the Korea Deep Space Ground System (KDGS) Is Essential
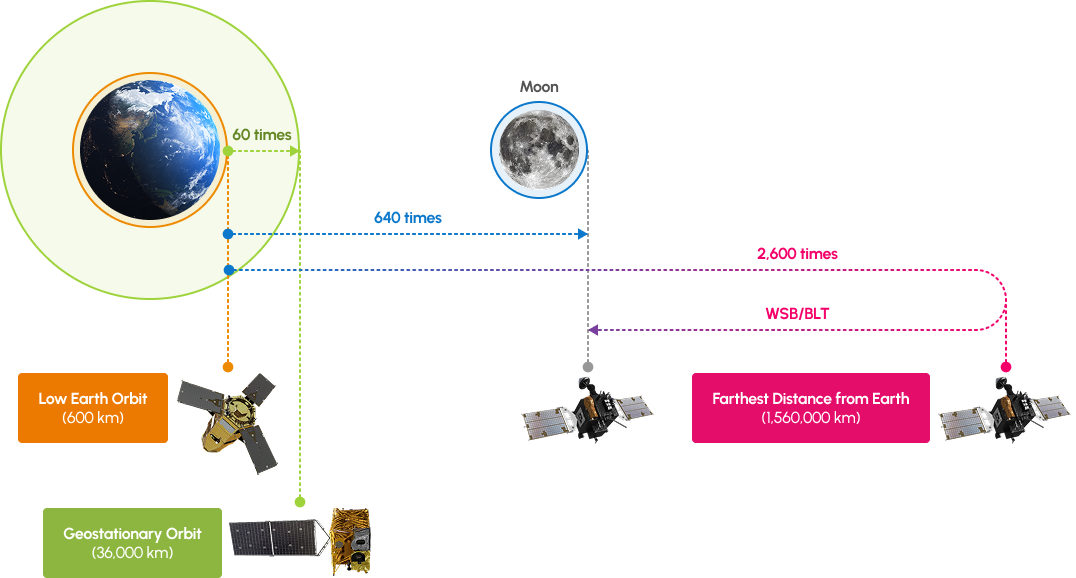
At its furthest distance from Earth, Danuri is approximately 1.56 million km (1.56 × 10⁶ km)— farther than low Earth orbit satellites like KOMPSAT (~600 km) or geostationary satellites like Chollian (~36,000 km). As a result, a dedicated deep space ground system is essential for communication and mission support.

Key Capabilities for Lunar Orbit Exploration
| Operator | Korea Aerospace Research Institute (KARI) |
|---|---|
| Location | Yeoju, Gyeonggi-do |
| Main Reflector Diameter | 35 m (largest in Korea) |
| Weight | 42.7m |
| Weight | 709.55 tons |
| Key Functions |
|
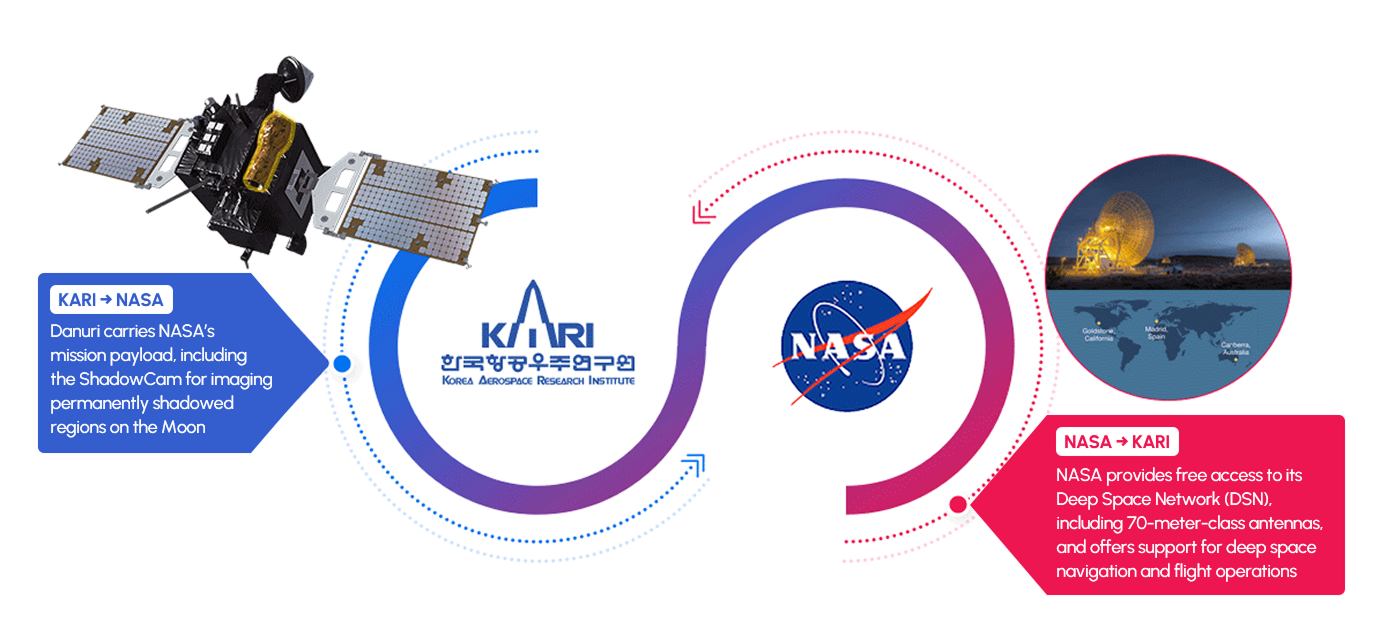
Collaboration with NASA