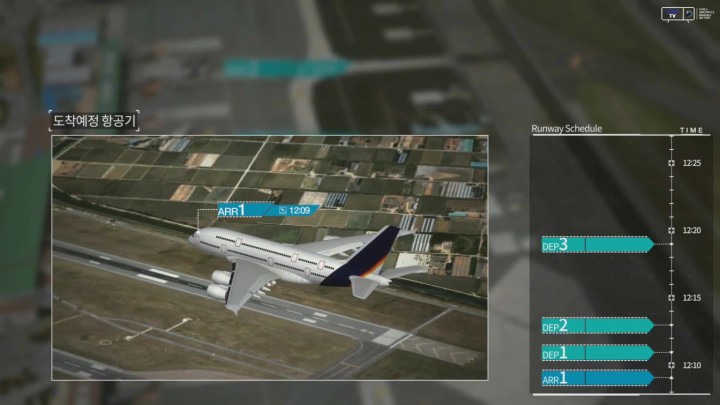
The next-generation aircraft departure and arrival management system, known as MIDAS (Management on Integrated Operations of Departure, Arrival, and Surface), is an advanced air traffic management solution designed to optimize the sequence and timing of aircraft movements during departures, arrivals, and taxiing at airports. Its primary objective is to alleviate delays and mitigate congestion in airports and surrounding airspace caused by increasing air traffic volume.
MIDAS is composed of two subsystems: the Departure Manager (DMAN) and the Terminal-Arrival Manager (T-AMAN). The DMAN subsystem uses a wide range of input data collected from airlines, air traffic control centers, and airport operators—along with predictive data on precise ground and in-flight aircraft trajectories—to calculate the optimal departure sequence and timing. This information is provided to air traffic controllers to support efficient aircraft departure operations.The T-AMAN subsystem forecasts precise trajectory information for inbound aircraft entering terminal control areas. Based on the Point Merge procedure, it generates optimized arrival schedules, enabling air traffic controllers to manage traffic flow efficiently in congested terminal approach areas and improve arrival sequencing.
MIDAS aims to reduce aircraft taxi and holding times, enhancing operational efficiency while also helping to lower fuel consumption and greenhouse gas emissions — major concerns for the global aviation industry.